ATTENTION: We are only offering PCR COVID-19 tests at this time. Rapid Testing NOT available.
Mobile HeaL is made possible by the support of various grants, partners and donations that allow us to bring health care to our communities. For these reasons not all services are available at every event and the services provided are determined by the obligation requirements established by the grants.
Services by clinic.
Services provided will vary by event and clinic type listed below.
Expand the tabs below for a list of services provided under our current Mobile HeaL clinics.
RMH: Rural Mobile Health
Services Provided:
Health Screenings
Includes: Blood Pressure Checks, Blood Sugar Analysis
Primary Care Services
Includes: Provider Consultations, Sick Visits, Wound Care, Health Education
COVID-19 Services
Includes: Testing (Rapid and PCR), Antiviral Treatment, Vaccines
Prescription Medication Refills
Includes: Writing prescription refills for various existing, known medications.
(Proof of medication required. No controlled substances)
COVID
Services Provided:
COVID-19
Includes: Rapid and PCR Testing, COVID-19 Vaccines, Treatment for COVID-19
*Any additional services provided at an event will always be indicated in the Event's Details found in the Mobile HeaL Clinic Calendar.
Mobile HeaL Services (A-Z)
See below for a description, information and additional resources regarding all services provided by Mobile HeaL.
Anemia / Iron Deficiency
What is Anemia?
Without enough iron, red blood cells can’t carry enough oxygen to body tissues. Iron deficiency often causes low blood cell levels (anemia) and can delay the development of unborn babies. Treatment includes iron supplements and a focus on any underlying causes.
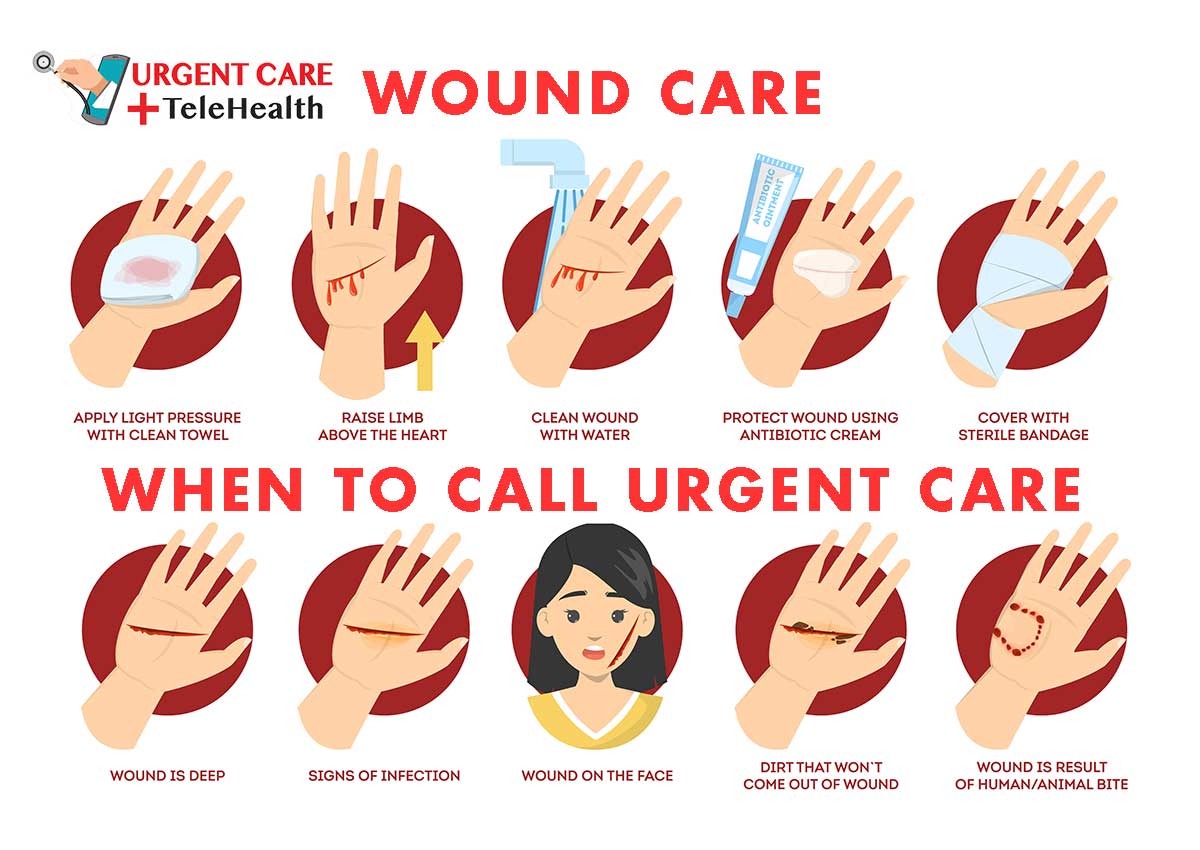
Basic Wound Care
Importance of Wound Care
Whether it’s a surgical wound or one that seemed minor at first but is getting worse instead of better, any wound that’s infected should be evaluated by a medical provider.
Signs a wound may be infected include:
• Increasing pain or redness
• Drainage or bleeding that won’t stop
• Fever and chills
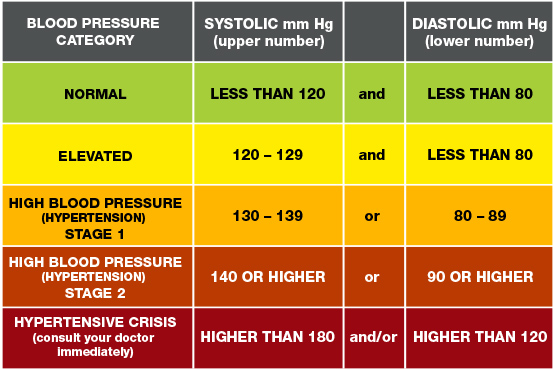
Blood Pressure (BP)
Understanding Blood Pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system.
Untreated, high blood pressure increases the risk of heart attack, stroke and other serious health problems. It’s important to have your blood pressure checked at least every two years starting at age 18.
Healthy lifestyle habits —such as not smoking, exercising and eating well — can help prevent and treat high blood pressure. Some people need medicine to treat high blood pressure.
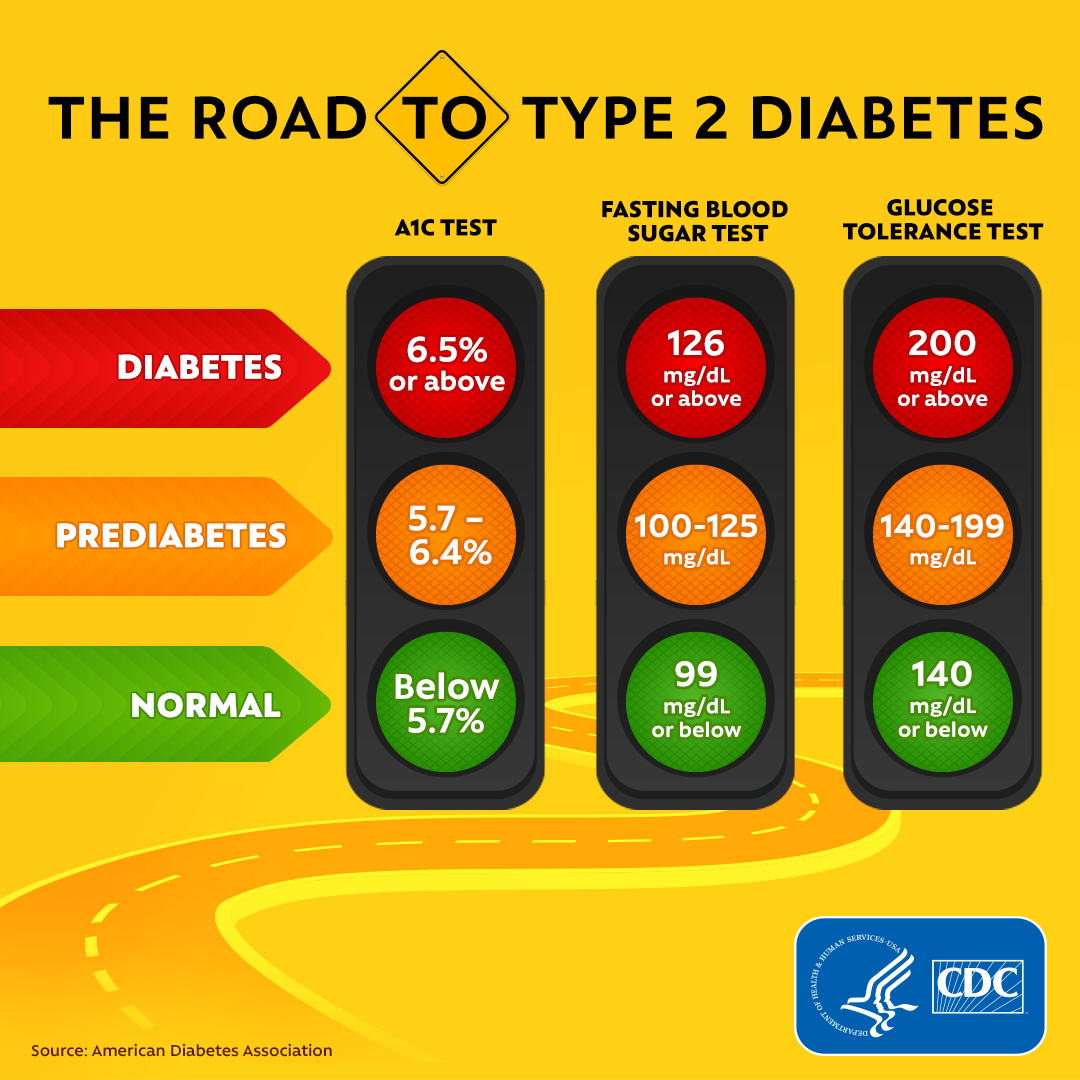
Blood Sugar and A1C
What is Blood Sugar and Hemoglobin?
Blood Sugar/Glucose and Hemoglobin (A1C) tests measure blood sugar levels and is commonly used to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes. Higher A1C levels are linked to diabetes complications.
Since glucose readings can drastically change throughout the course of a day — based on diet choices, physical activity, stress levels, etc.— A1c tests are more accurate and helpful to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes.
Blood Oxygen Saturation (O2)
About Blood Oxygen Saturation
Oxygen saturation, or "O2 sat" for short, is a measure of how much oxygen is in your blood. Oxygen travels through your bloodstream via a protein in your red blood cells called hemoglobin. Every cell in your body needs oxygen to work.
For most healthy adults, a normal oxygen saturation level is between 95% and 100%. An oxygen saturation level below this range requires medical attention because it means your body isn't getting enough oxygen.
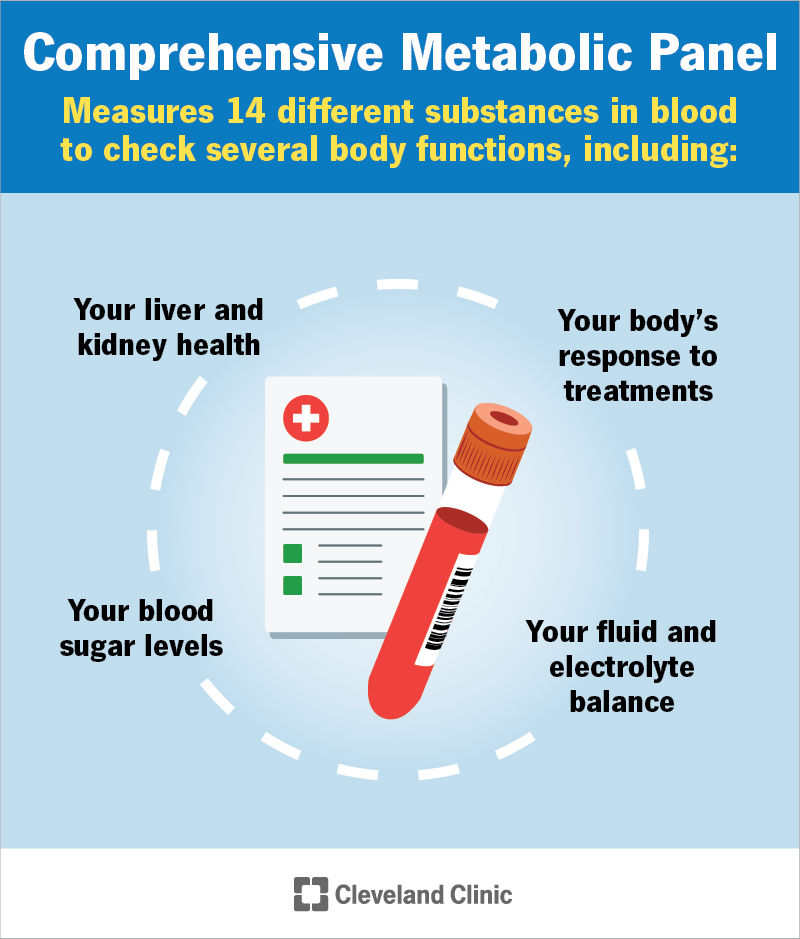
Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP)
What is a Comprehensive Metabolic Panel?
A comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP) is a blood sample test that measures 14 different substances in your blood. It provides important information about your body's chemical balance and metabolism (how your body transforms the food you eat into energy).
Healthcare providers often use a CMP as a routine blood test and to help diagnose, screen for or monitor certain health conditions.
COVID-19: Testing
When to Get Tested for COVID-19.
- If you have symptoms, test immediately.
- If you were exposed to COVID-19 and do not have symptoms, wait at least 5 full days after your exposure before testing. If you test too early, you may be more likely to get an inaccurate result.
- If you are in certain high-risk settings, you may need to test as part of a screening testing program.
- Consider testing before contact with someone at high risk for severe COVID-19, especially if you are in an area with a medium or high COVID-19 Community Level.
For guidance on using tests to determine which mitigations are recommended as you recover from COVID-19, go to Isolation and Precautions for People with COVID-19.
COVID-19 Testing at Mobile HeaL
At this time Mobile HeaL only offers PCR COVID-19 testing.
- PCR tests – Typically the most reliable tests for people with or without symptoms. These tests detect viral genetic material, which may stay in your body for up to 90 days after you test positive. Therefore, you should not use a NAAT if you have tested positive in the last 90 days.
COVID-19: Vaccines
About COVID-19 Vaccines
COVID-19 vaccines available in the United States are effective at protecting people from getting seriously ill, being hospitalized, and dying. As with other vaccine-preventable diseases, you are protected best from COVID-19 when you stay up to date with the recommended vaccinations, including recommended boosters.
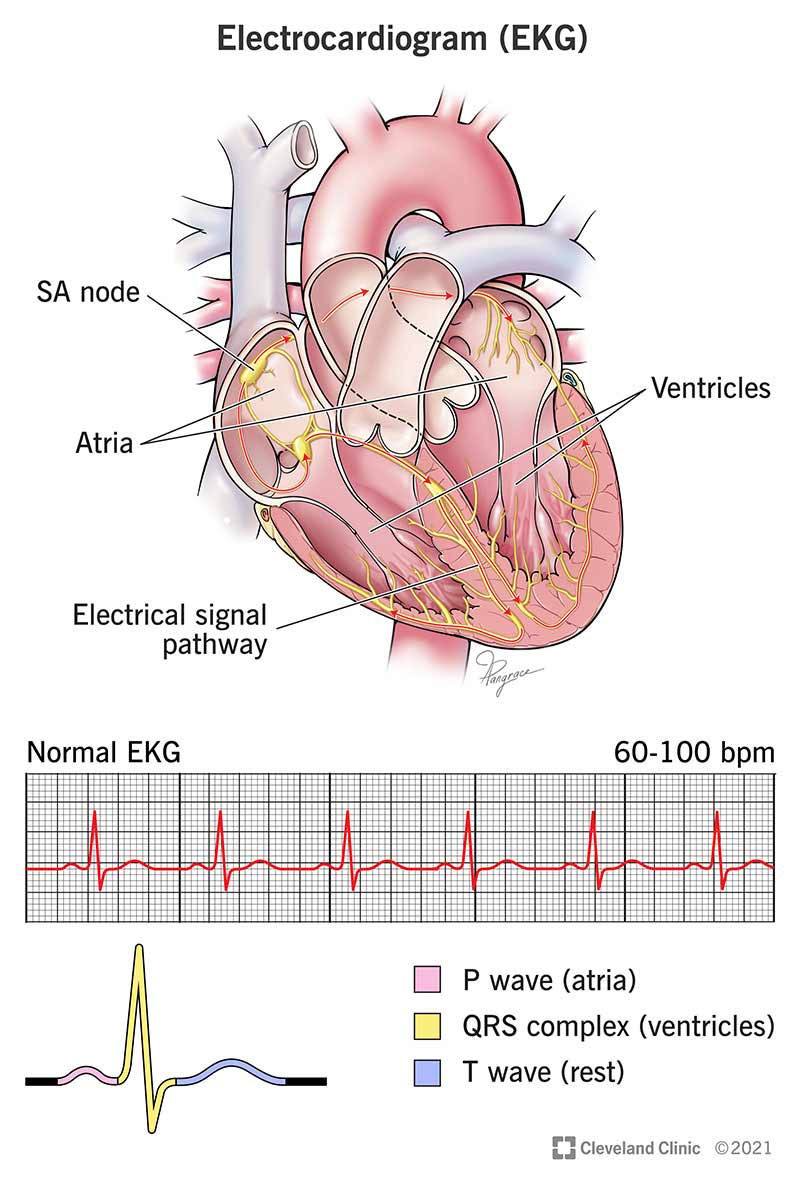
Electrocardiogram (EKG)
What is an Electrocardiogram?
An EKG test is an easy way to get information to diagnose a problem with your heart. It doesn’t take long and doesn’t cause pain, but an electrocardiogram test can tell your healthcare provider if you’ve had a heart attack, heart failure or heart damage. It can also tell them if your heart rhythm isn’t normal or how well your pacemaker is working.
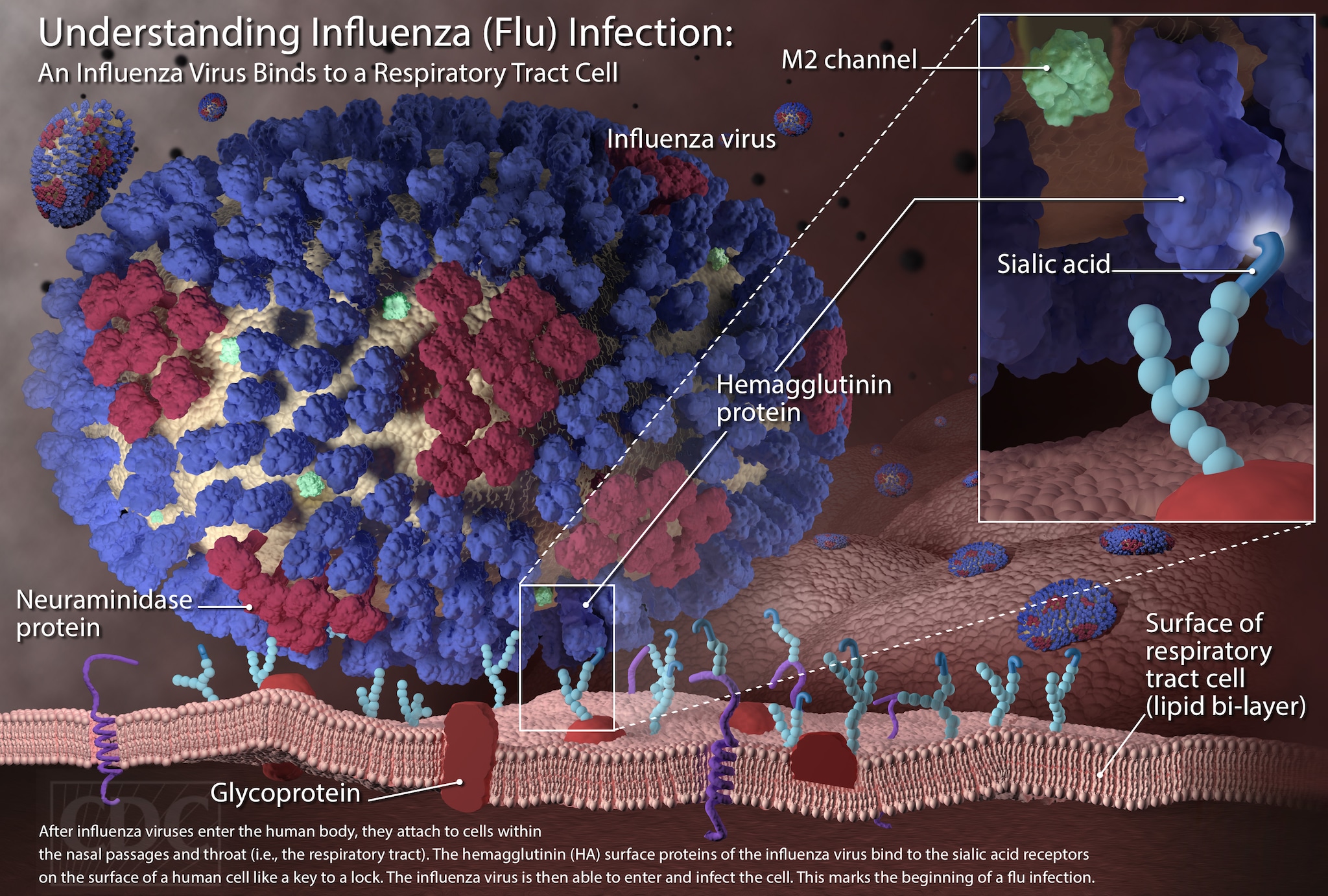
Flu Shots
What is Influenza?
Influenza (flu) is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses that infect the nose, throat, and lungs. Some people, such as people 65 years and older, young children, and people with certain health conditions, are at higher risk of serious flu complications.
The best way to reduce the risk of flu and its potentially serious complications is by getting vaccinated each year.
HIV Screenings
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) damages the immune system and interferes with the body's ability to fight infection and disease. HIV can be spread through contact with infected blood, semen, or vaginal fluids.
CDC recommends that everyone between the ages of 13 and 64 should get tested for HIV at least once as part of routine health care. People should get tested more often when they have had more than one sex partner or are having sex with someone whose sexual history they don’t know. Some sexually active gay and bisexual men may benefit from more frequent testing (e.g., every 3 to 6 months).

Liver Panel
Why is a Liver Test Important?
Liver function tests (LFTs), also referred to as hepatic function tests, a liver panel, or liver enzymes, are blood tests that measure several enzymes and proteins. This test measures how well the liver is working as well as the blood levels of total protein, albumin, bilirubin, and liver enzymes. High or low levels may mean that liver damage or disease is present.
Elevated or decreased concentration of liver enzymes provides your healthcare provider with information that can be used to identify liver disease and, sometimes, diagnose the type of liver disease.
MPox or MPX
What is Mpox?
Mpox or MPX is a rare disease that is caused by infection with the MPX virus. Symptoms of Mpox are similar to, but milder than the symptoms of smallpox. The main differences between them is that Mpox causes lymph nodes to swell while smallpox does not.
Symptoms May Include
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle aches
- Backache
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Chills
- Exhaustion
- Macules
- Papules
- Vesicles
- Pustules
- Scabs
Getting Vaccinated: Jynneos
JYNNEOS is a 2-dose vaccine developed to protect against mpox and smallpox infections. People need to get both doses of the vaccine for the best protection against Mpox. The second dose should be given 4 weeks after the first dose.
Nalaxone Distribution
What is Nalaxone?
Commonly known as Narcan, Naloxone is a medication approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) designed to rapidly reverse opioid overdose. It is an opioid antagonist—meaning that it binds to opioid receptors and can reverse and block the effects of other opioids, such as heroin, morphine, and oxycodone.
Uses: It can treat narcotic overdose in an emergency situation.
Prescription Medication Refills
Prescription Medication Refills at Mobile HeaL
Prescription medications are pharmaceutical drugs that are only permitted to be dispensed to those with a medical prescription.
We recognize that patients face many challenges within the health care system that can make it difficult to get access to the prescriptions they need and their refills. To break these barriers, Mobile HeaL will write prescription refills for patients with diagnosed chronic conditions including; high blood pressure, diabetes, asthma, and more.
*We do not keep or provide any prescription medications on site.
**No prescription refills available for controlled substances.
Mental Health Services
What is mental health?
Mental health includes our emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It affects how we think, feel, and act. It also helps determine how we handle stress, relate to others, and make healthy choices.1 Mental health is important at every stage of life, from childhood and adolescence through adulthood.
Although the terms are often used interchangeably, poor mental health and mental illness are not the same. A person can experience poor mental health and not be diagnosed with a mental illness. Likewise, a person diagnosed with a mental illness can experience periods of physical, mental, and social well-being.
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
What are STIs?
A Sexually Transmitted Infection (STI) is an infection passed from one person to another person through sexual contact. An infection is when a bacteria, virus, or parasite enters and grows in or on your body. STIs are also called sexually transmitted diseases, or STDs. Some STIs can be cured and some STIs cannot be cured.
Common STIs and Symptoms:
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
An infection that causes warts in various parts of the body, depending on the strain.
Genital Herpes
A common sexually transmitted infection marked by genital pain and sores.
Chlamydia
Many who have chlamydia don't develop symptoms, but they can still infect others through sexual contact. Symptoms may include genital pain and discharge from the vagina or penis.
Gonorrhea
A sexually transmitted bacterial infection that, if untreated, may cause infertility.
HIV/AIDS
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) or Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS), damages the immune system and interferes with the body's ability to fight infection and disease. HIV can be spread through contact with infected blood, semen, or vaginal fluids.
Syphilis
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease (STD) caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. Syphilis can cause serious health effects without adequate treatment.
Thyroid
What Is the Thyroid?
The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the base of the neck just below the Adam's apple. Although relatively small, the thyroid gland plays a huge role in our body, influencing the function of many of the body’s most important organs, including the heart, brain, liver, kidneys and skin. Ensuring that the thyroid gland is healthy and functioning properly is vitally important to the body's overall well-being.
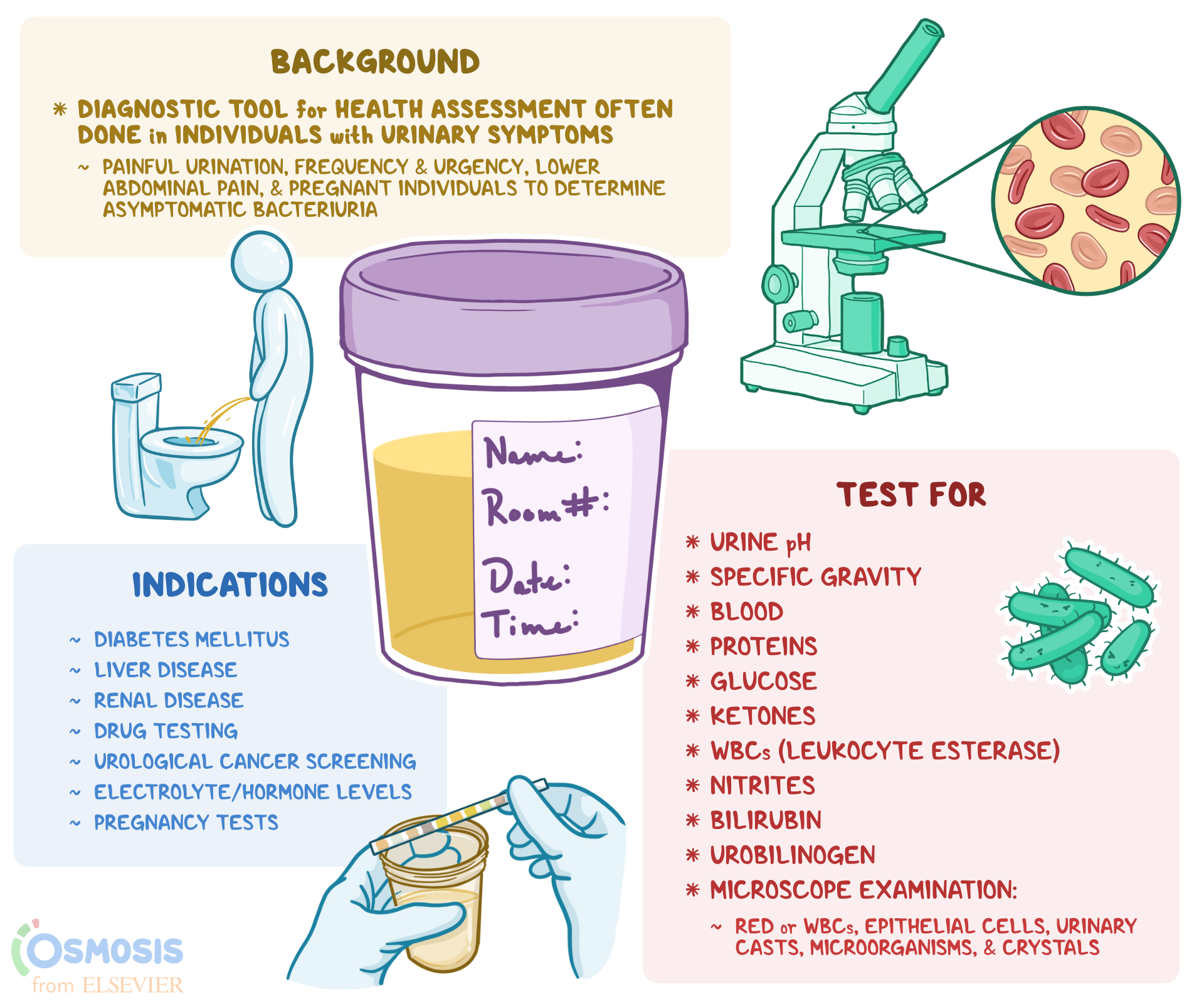
Urinalysis
What is a Urinalysis?
A urinalysis is a test of your urine. It's used to detect and manage a wide range of disorders, such as urinary tract infections, kidney disease and diabetes. A urinalysis involves checking the appearance, concentration and content of urine.
Vaginitis
What is Vaginits?
Vaginitis is an inflammation of the vagina that can result in discharge, itching and pain. The cause is usually a change in the balance of vaginal bacteria or an infection. Reduced estrogen levels after menopause and some skin disorders also can cause vaginitis.
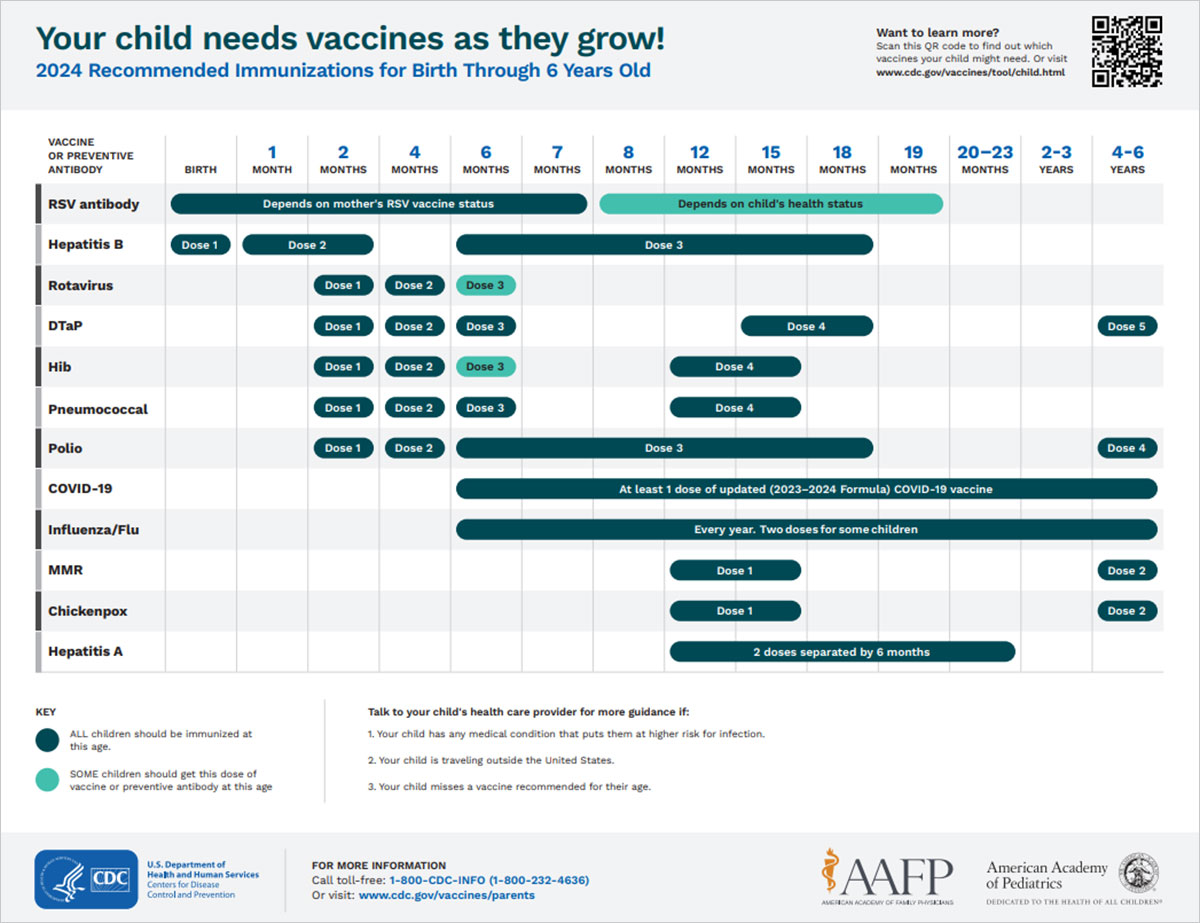
Youth Vaccinations
Youth Vaccinations
On-time vaccination throughout childhood is essential because it helps provide immunity before children are exposed to potentially life-threatening diseases. Vaccines are tested to ensure that they are safe and effective for children to receive at the recommended ages.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/anemia-after-surgery-3156852-Final-63c258f51d7846e1b24d870a3b8ea88c.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/red-blood-cells--beautiful-scientific-background--628279656-9c8737d966724401b481e82952e6e21d.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/3157004_color-5b9bba7646e0fb0050385b56.png)